Working personnel in all types of industries must have the knowledge of the types of occupational health and safety hazards in order to take steps to minimize these hazards for a safer and healthier workplace. But what is a Hazard? Hazard is defined as the “source or situation that carries a potential to cause injury and ill health”
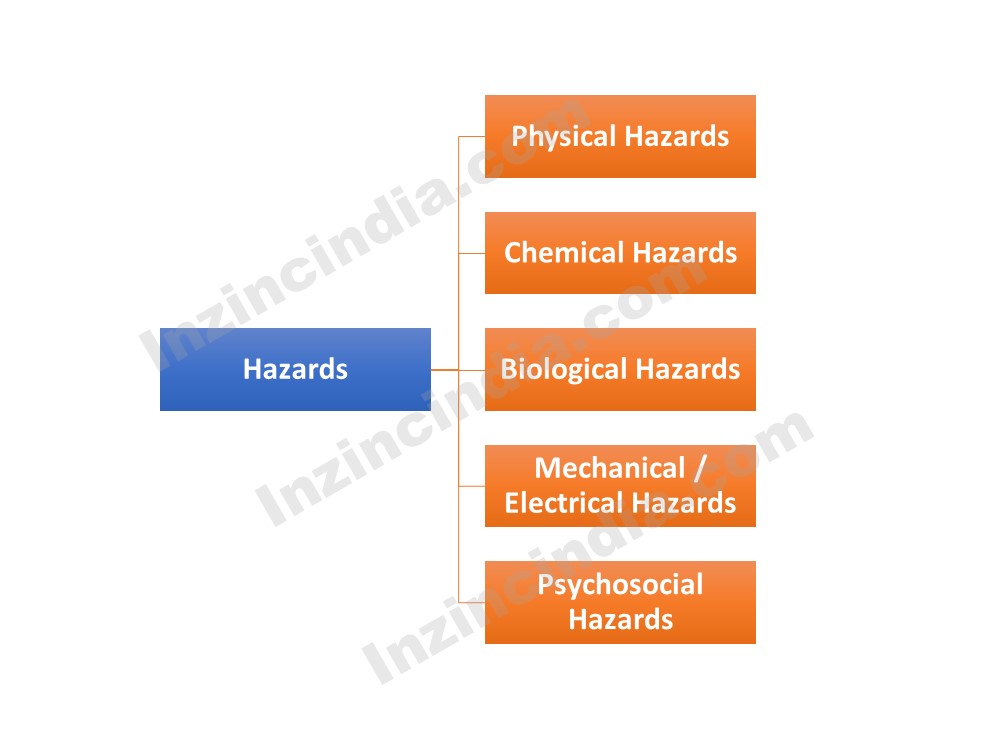
Physical hazards – Types of occupational physical hazards
Physical hazards are those occupational hazards that has the potential to cause or threaten the physical safety of personnel working for an organization.
Examples of physical hazards
Following are few examples of physical hazards that are common in Organizations / industries:
- Slippery or uneven ground
- Working at Heights

- Poor Ergonomics
- Extreme Heat / Cold
- Fire and explosion
- Ionizing Radiation (radiation that carries X-rays, Gamma Rays, etc that can have health effects such as human tissue damage)
- Noise
- Vibration
- Confined Spaces
Chemical hazards – Types of Occupational chemical hazards
OHS Chemical hazards are the hazards that are present when you are exposed to any chemical preparation (solid, liquid or gas) in the workplace.
Examples of chemical hazards
Below are few examples of chemical hazards that are common in Organizations / industries using chemicals for producing their products or providing their services:
- exposure to vapours and toxic fumes (Ex: welding fumes)
- cleaning products and solvents (Ex: Phthalates used in household cleaning products)
- continuous / long term exposure to harmful chemicals (Ex: Benzene chemical is carcinogenic or cancer causing)
- carbon monoxide or other gases
- gasoline or other flammable materials
Biological hazards – Types of occupational biological hazards
Biological hazards are those types of occupational health and safety hazards that come from working with people, animals or infectious plant material.
Examples of biological hazards
Some of the examples of biological hazards include:
- blood or other bodily fluids
- air-borne pathogens (like influenza)
- Bacteria and viruses
- Mold and fungus
- insect bites
- sewage
- animal and bird droppings
- stagnant water forming breeding ground for mosquitoes
Mechanical and electrical hazards – Types of occupational mechanical / electrical hazards
Mechanical hazards are the occupational hazards leading to injuries to individuals arising from sources such as machinery, its parts, tools, objects and materials processed or used in the work process.
Electrical hazards arise when an individual comes into contact with energized equipment or a conductor which leads to serious / fatal injuries to the individual.
Examples of mechanical hazards
Few examples of mechanical hazards include:
- unguarded machinery leading to entanglement of the cloth of the worker or any body part with moving parts of the machinery leading to injuries and fatalities

- cutting
- crushing
- shearing
- entrapment
- impact
- friction and abrasion, etc.
Examples of electrical hazards
Below are some of the examples of electrical hazards:
- Overloaded circuit

- live exposed cables or wires
- faulty wires
- frayed cords
- deteriorated insulation of wires
- poor or inadequate wiring
- potential flammable materials kept in the vicinity of electrical equipment leading to possible explosions / fire
- damp / wet conditions
- contact with overhead power lines
- improper grounding
Psychosocial hazards – Types of occupational psychosocial hazards
Psychosocial hazards are the occupational hazards that affect the individual psychologically due to stressors at the work place. Psychosocial hazards lead to emotional problems and depression that eventually affects work in a negative way. A pschologically stressed individual can be a potential source of workplace accidents / incidents.
Psychosocial hazard examples
- Psychosocial hazards include but are not limited to mental stress, violence and other workplace stressors.

- Risks to psychological health at the workplace may arise from organisational or personal factors, with the major factors being
- poor design of work and jobs
- poor communication and interpersonal relationships
- bullying, victimization, occupational violence and fatigue
- work harassment including sexual harassment
- repetitive tasks
- working over time
- personal problems and tensions of the individual
- burnout due to prolonged stress
Article by Sudhir G K, Management Consultant
The above types of occupational health and safety hazards can be used to train Organizational personnel and other relevant interested parties to ensure basic awareness of these OHS hazards so that workplace incidents can be minimized.
